Skin Cancer Risk Factors
Skin cancer risk factors - Everyone can get skin cancer. But there are factors that clearly increase the risk of skin cancer.
The most important risk factors for skin cancer at a glance:
In most cases, skin cancer is the result of too much exposure to UV radiation. This UV radiation occurs naturally in sunlight. In addition, UV radiation is artificially generated in solar equipment such as tanning beds, sunsets, and solariums. If the skin is exposed to UV radiation too often and for too long, the skin cells may be damaged. Skin cancer may be the result in the long term.
In addition to the number of UV rays that your skin absorbs during your life, the skin type also plays a role. People with light skin who burn quickly in the sun have a greater risk of developing skin cancer than dark people with a lot of pigment in their skin.
The development of skin cancer is related to:
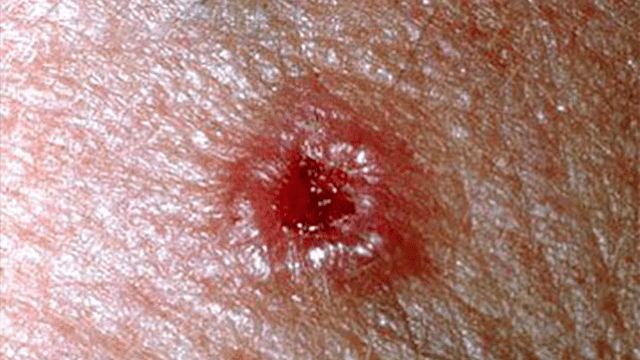
Skin cancer is often the result of too much exposure to UV radiation. Protection against overexposure to the sun is therefore of great importance. In addition, you must monitor changes in moles (color and size).
How can you sunbathe wisely?
The most important risk factors for skin cancer at a glance:
- Excessive exposure to the sun is seen as the main cause for the development of skin cancer. But also UV radiation from tanning beds is dangerous! The UV radiation from the sun and the sunbed must be added together.
- Anyone who has been in the sun as a child is more at risk of developing basal cell cancer later in life. The higher the UV load, the greater the risk.
- The number of times someone burns. Every time you burn (as a child or as an adult), the chance that you get skin cancer increases.
- People with fair skin (skin type I and II) are naturally more sensitive to UV radiation. If you have this type of skin, the sun is more harmful to you than to other people.
- People over 50 have a greater risk of developing skin cancer Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are therefore mainly seen from the age of fifty. A melanoma can also occur at a younger age.
- If you have many birthmarks (more than fifty), you run a higher risk of developing a melanoma.
- Some forms of skin cancer are hereditary.
- When you work outside or have lived in the tropics, you have a greater chance of getting skin cancer.
- If you take medicines that suppress the immune system, for example after an organ transplant.
In most cases, skin cancer is the result of too much exposure to UV radiation. This UV radiation occurs naturally in sunlight. In addition, UV radiation is artificially generated in solar equipment such as tanning beds, sunsets, and solariums. If the skin is exposed to UV radiation too often and for too long, the skin cells may be damaged. Skin cancer may be the result in the long term.
In addition to the number of UV rays that your skin absorbs during your life, the skin type also plays a role. People with light skin who burn quickly in the sun have a greater risk of developing skin cancer than dark people with a lot of pigment in their skin.
The development of skin cancer is related to:
- The total amount of ultraviolet radiation that a person gains in the course of his life. The ultraviolet radiation from the sun and sun equipment must be added together.
- Excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation during childhood (up to about 15 years). The higher the UV burden on the youth, the greater the risk of basal cell cancer in later life.
- The number of times someone burns. As a person burns more often in his life, the risk of skin cancer increases.
- The interaction between ultraviolet radiation and cosmetics and tanning agents containing psoralen.
Skin cancer is often the result of too much exposure to UV radiation. Protection against overexposure to the sun is therefore of great importance. In addition, you must monitor changes in moles (color and size).
How can you sunbathe wisely?
- Protect your skin with protective clothing, a sun hat, and sunglasses.
- Lubricate generously and several times a day with an anti-sunscreen with a higher protection factor.
- Do not sunbathe between 11-15 hours; in that period most of the UV radiation from the sunlight penetrates the skin.
- Allow the skin to become accustomed to the sun and avoid burning.
- Preferably avoid sunbeds.
- Protect children from the sun sufficiently.
*Image source : Healthline
References :
Post a Comment for "Skin Cancer Risk Factors"