Toenail Cancer Symptoms
What is a subungual melanoma?
A melanoma is a form of skin cancer, which results from the melanocytes. A subungual melanoma is a variant of the acrolentigine melanoma, located on the palms and the soles of the foot, and below or around the nails. A subungual melanoma is usually found under the nail of a thumb or big toe, but any fingernail or toenail can be affected. The subungual melanoma is thus located under the nail. Often it is misunderstood and wrongly for an innocent deviation as it is. A subungual melanoma has various forms of expression. It can be seen as:
A subungual melanoma must be distinguished from a subungual hematoma, the medical name of blood subcutaneous nail . There must always be a history such as bumps, an object on the nail, jogging / jogging, other trauma, the use of blood thinners, etc. If that is not the case, then the distinction between a subungual Melanoma with a subungual melanoma difficult to make. A nasal discharge of blood shifts as the nail grows. That is clearly not the case with a melanoma.
Who does the subungual melanoma occur for?
The subungual melanoma is a rare skin condition. Only about 1% of all melanomas in people with a slight skin color are a subungual melanoma. It develops in people of all ethnic backgrounds, regardless of their skin tone. A melanoma of the skin is a relatively rare phenomenon in people with dark skin, but a subungual melanoma occurs approximately equally for each skin type. The literature shows that 20% of all melanomas in skin type V and VI (dark skin) are under the nail, while skin type I and II (light skin) is only 1%. It is therefore the most common form of melanoma in deeply pigmented individuals. The subungual melanoma is most common in people between the ages of 40 and 70 years.
Recognize a subungual melanoma (Toenail cancer symptoms)
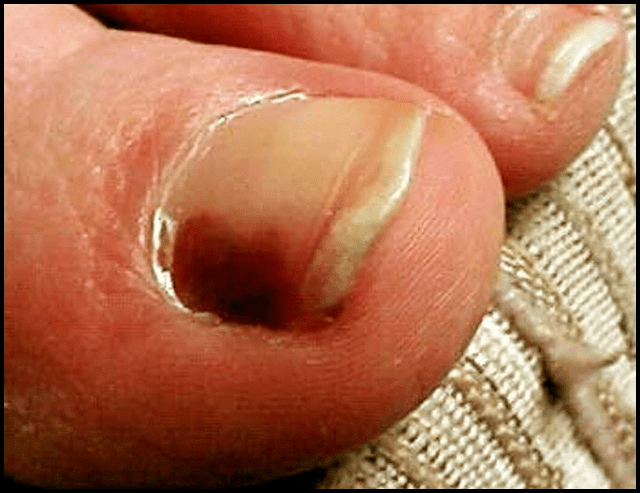
How and what can you recognize a subungual melanoma? A subungual melanoma often begins as a brown band in the longitudinal nail (melanonycia striata), a solitary brown stripe. Over time (weeks to months), the brown (pigment) band becomes wider, especially at its proximal end (the edge surrounding the nail plate) and irregular in pigmentation, including light brown and dark brown. Also, a tumor or nodule can develop that can swear or bleed. In addition, nail dystrophy may occur, with the nail becoming thinner, bursting or deformation.
Amelanotic melanoma
In half of the cases it is an amelanotic melanoma, with no pigment visible. There may be a tumor or nodule underneath the nail plate, which can lead to a nail lesion (either onycholysis ). It can sometimes look like a wart . It is usually painless, but an invasive tumor can displace the underlying structures and cause severe pain.
In the case of a melanoma, the so-called Hutchinson's sign can be present. This indicates a brown discoloration of the skin of the toenail or fingernail belt. This discoloration is caused by pigment of ingrown melanoma cells. These extend from a subungual melanoma. But in a hematoma, this is sometimes the case. Therefore, the Hutchinson's sign does not make any difference; It is rather an indication or indication.
Subungual melanoma treatment
A subungual melanoma must be removed surgically. This requires the removal of the melanoma by a certain margin. Often the distal cot (the end of the finger or toe) is amputated. Sometimes the surgeon can leave a part of the bowel intact, provided that the required margin (according to the treatment protocol) allows this. Removal of local lymph nodes does not contribute to survival chances according to literature.
A melanoma is a form of skin cancer, which results from the melanocytes. A subungual melanoma is a variant of the acrolentigine melanoma, located on the palms and the soles of the foot, and below or around the nails. A subungual melanoma is usually found under the nail of a thumb or big toe, but any fingernail or toenail can be affected. The subungual melanoma is thus located under the nail. Often it is misunderstood and wrongly for an innocent deviation as it is. A subungual melanoma has various forms of expression. It can be seen as:
- A tumor;
- A longitudinal brown tire in the nail (melanonycia striata), so in the longitudinal direction; or
- A diffuse (wide variety) brown-black discoloration of the nail.
A subungual melanoma must be distinguished from a subungual hematoma, the medical name of blood subcutaneous nail . There must always be a history such as bumps, an object on the nail, jogging / jogging, other trauma, the use of blood thinners, etc. If that is not the case, then the distinction between a subungual Melanoma with a subungual melanoma difficult to make. A nasal discharge of blood shifts as the nail grows. That is clearly not the case with a melanoma.
Who does the subungual melanoma occur for?
The subungual melanoma is a rare skin condition. Only about 1% of all melanomas in people with a slight skin color are a subungual melanoma. It develops in people of all ethnic backgrounds, regardless of their skin tone. A melanoma of the skin is a relatively rare phenomenon in people with dark skin, but a subungual melanoma occurs approximately equally for each skin type. The literature shows that 20% of all melanomas in skin type V and VI (dark skin) are under the nail, while skin type I and II (light skin) is only 1%. It is therefore the most common form of melanoma in deeply pigmented individuals. The subungual melanoma is most common in people between the ages of 40 and 70 years.
Recognize a subungual melanoma (Toenail cancer symptoms)
How and what can you recognize a subungual melanoma? A subungual melanoma often begins as a brown band in the longitudinal nail (melanonycia striata), a solitary brown stripe. Over time (weeks to months), the brown (pigment) band becomes wider, especially at its proximal end (the edge surrounding the nail plate) and irregular in pigmentation, including light brown and dark brown. Also, a tumor or nodule can develop that can swear or bleed. In addition, nail dystrophy may occur, with the nail becoming thinner, bursting or deformation.
Amelanotic melanoma
In half of the cases it is an amelanotic melanoma, with no pigment visible. There may be a tumor or nodule underneath the nail plate, which can lead to a nail lesion (either onycholysis ). It can sometimes look like a wart . It is usually painless, but an invasive tumor can displace the underlying structures and cause severe pain.
In the case of a melanoma, the so-called Hutchinson's sign can be present. This indicates a brown discoloration of the skin of the toenail or fingernail belt. This discoloration is caused by pigment of ingrown melanoma cells. These extend from a subungual melanoma. But in a hematoma, this is sometimes the case. Therefore, the Hutchinson's sign does not make any difference; It is rather an indication or indication.
Subungual melanoma treatment
A subungual melanoma must be removed surgically. This requires the removal of the melanoma by a certain margin. Often the distal cot (the end of the finger or toe) is amputated. Sometimes the surgeon can leave a part of the bowel intact, provided that the required margin (according to the treatment protocol) allows this. Removal of local lymph nodes does not contribute to survival chances according to literature.
Post a Comment for "Toenail Cancer Symptoms"