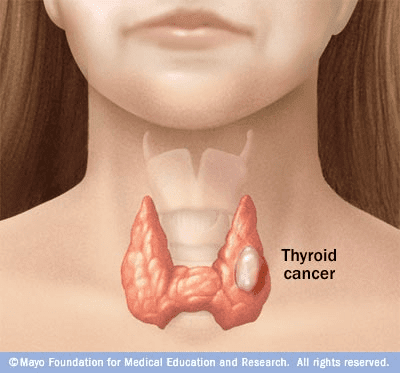
Causes And Symptoms Of Thyroid Cancer
The causes of thyroid cancer are not always known. There are factors that increase the risk.
Thyroid cancer is suspected when the following appears:
Thyroid cancer: diagnostic studies
The diagnosis is mainly based on ultrasound and scintigraphy.
In this way, the treatment is always adjusted as much as possible to the individual. The doctors will propose a treatment tailored to your specific situation, including the following elements:
Also for this cancer, the MOC will outline the best route, yet we give below an overview of the most used options.
Surgery
Depending on the number of tumor foci, one half or the entire thyroid gland is surgically removed (thyroidectomy). The glands surrounding the thyroid gland can then also be removed (gland clearing) to check whether they have been affected by cancer cells from the tumor.
Radioactive iodine
In case of a local expansion or metastases, tests are carried out to check whether the tumor cells hold the iodine. If so, they can be destroyed by injecting a high dose of iodine 131.
Radiotherapy and/or chemotherapy
In certain cases, a classic radiography or chemotherapy is possible.
Life after thyroid cancer
As a result of the treatment, there is often a shortage of thyroid hormone during the rest of life. The intake of the thyroid hormone, adjusted according to blood dosages, compensates for the absent or inadequate production by the thyroid gland of this hormone, which is indispensable for the proper functioning of the body. A lifelong follow-up is therefore necessary.
- An irradiation in the neck area, especially during childhood. The tumor can emerge decades later.
- An infection by radioactive iodine . Attention: the administration of small doses of radioactive products to make a diagnosis (eg a scintigraphy) does not pose a particular risk.
Thyroid cancer is suspected when the following appears:
- a nodule at the bottom of the neck
- a lymph gland
- a goiter that suddenly gets bigger
- a persistent hoarseness due to the paralysis of a vocal cord
Thyroid cancer: diagnostic studies
The diagnosis is mainly based on ultrasound and scintigraphy.
- The ultrasound determines the size of the lump and its nature ( hard, liquid or mixed).
- In a scintigraphy radioactive iodine is injected to study its adhesion through the nodule. One speaks of a cold lump when the bond is weak, and of a warm lump when the bond is strong.
- a cytop function of the nodule, followed by a microscopic analysis of the removed cells. The cytop function is a painless examination that is simply done during the consultation.
In this way, the treatment is always adjusted as much as possible to the individual. The doctors will propose a treatment tailored to your specific situation, including the following elements:
- the type of cancer
- the stage (the extent) of cancer;
- the general state of health of the patient.
Also for this cancer, the MOC will outline the best route, yet we give below an overview of the most used options.
Surgery
Depending on the number of tumor foci, one half or the entire thyroid gland is surgically removed (thyroidectomy). The glands surrounding the thyroid gland can then also be removed (gland clearing) to check whether they have been affected by cancer cells from the tumor.
Radioactive iodine
In case of a local expansion or metastases, tests are carried out to check whether the tumor cells hold the iodine. If so, they can be destroyed by injecting a high dose of iodine 131.
Radiotherapy and/or chemotherapy
In certain cases, a classic radiography or chemotherapy is possible.
Life after thyroid cancer
As a result of the treatment, there is often a shortage of thyroid hormone during the rest of life. The intake of the thyroid hormone, adjusted according to blood dosages, compensates for the absent or inadequate production by the thyroid gland of this hormone, which is indispensable for the proper functioning of the body. A lifelong follow-up is therefore necessary.
*Image source : Mayo Clinic
References :
Post a Comment for "Causes And Symptoms Of Thyroid Cancer"