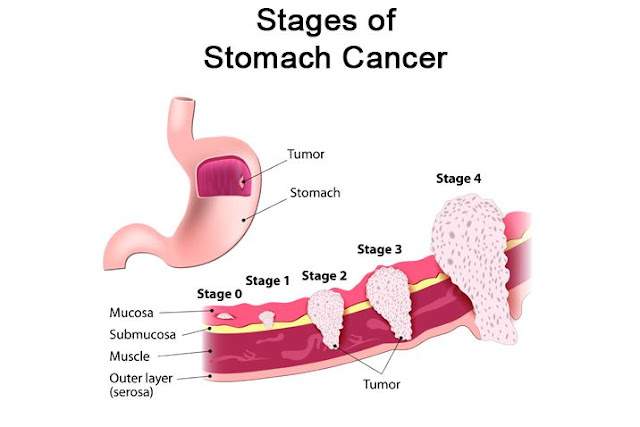
Stage 4 Stomach Cancer Symptoms
Stomach cancer usually does not give rise to complaints at an early stage. At stage 4 means that your cancer is advanced and has spread to body organs further away from the stomach, such as the lungs, brain or bones. Stomach cancer symptoms may occur :
The symptoms do not have to indicate stomach cancer. They can also be caused by other conditions. If you have complaints for 3 to 4 weeks, please go to your GP. Even if you have a black stool for several days and do not use iron pills.
Surviving stomach cancer
Of the patients with stomach cancer stage 1, after 1 year more than 80% and after almost 3 years, almost 70% live. In patients with stage 4 stomach cancer, less than 20% after 1 year is still alive. The survival of stomach cancer has hardly been improved over time.
Stomach cancer risk factors
The exact cause of stomach cancer is unknown. There are, however, factors that increase the risk of stomach cancer.
Infection with bacteria
A greater risk of stomach cancer is caused by infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. This bacterium can cause chronic inflammation of the stomach wall and stomach ulcers. Many years later this can lead to stomach cancer.
The Helicobacter pylori are transmitted by mouth and contaminated food. Infection with this bacterium does not mean that you automatically get stomach cancer.
Contamination with Helicobacter pylori is less common in the Western world. As a result, the number of people with stomach cancer decreases in developed countries.
Lifestyle
The number of lifestyle factors increase or decrease the risk of stomach cancer:
A number of medical conditions may increase the risk of stomach cancer.
Removal of part of the stomach
As a result, there is a higher risk of cancer in the remaining part of the stomach. This is because less gastric acid is made. As a result, more bacteria can grow in the stomach. These can help to produce more chemicals that can increase the risk of stomach cancer.
Insufficient gastric acid
Gastric acid is a juice in the stomach that consumes the food. Too low levels of gastric acid is a risk factor for gastrointestinal cancer. It can also cause other complaints, such as pernicious anemia. This is a condition in which patients do not adequately take vitamin B12 from the diet. As a result, they have an increased risk of anemia: a lack of red blood cells.
The insufficient gastric acid may have different causes. The medical term for insufficient stomach acid is achlorhydric.
Gastroesophageal reflux
In this condition, gastric acid rises in the esophagus. This increases the risk of cancer at the transition between gastrointestinal and esophagus.
Chronic atrophic gastritis
This is a chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract.
Adenomatous polyps in the stomach
Adenomatous polyps are benign swings. In the stomach, they rarely occur. Most people with polyps in the stomach have the hereditary disorder polyposis.
Hereditary cancer for stomach cancer
About 5% of people with stomach cancer get the disease through a hereditary plant. There are families with hereditary cancer for stomach cancer.
Also, there are some rare hereditary conditions that can cause various tumors, including stomach cancer. It is usually about Lynch's syndrome.
If you have questions about heredity in the event of your illness, please discuss it with your GP or specialist.
Not contagious
Cancer is not contagious. Also stomach cancer not. Also by saliva, vomiting or stools, you can not get infected.
Treatment of stomach cancer
The stage of your cancer helps your doctor to decide what treatment you need. Treatment also depends on:
- Weight loss. Weight loss due to less appetite and a dislike of particular food. Especially products that smell strong like coffee, roast meat, broth, herbs, and spices can reluctantly generate.
- Ache. A painful feeling in the stomach region, nausea and a full feeling in the upper abdomen.
- Persistent indigestion (dyspepsia) and burping. Some people are more affected by air buildup. You can also suffer from acid fires: a burning, squeezing or convulsive feeling behind the sternum. Acid fires are caused by gastric acid flowing back into the esophagus.
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia). You may feel that the food does not want to fall and stays stuck behind the sternum. This is called 'passenger complaints'. These complaints may occur in a tumor associated with the stomach ulcer or at the stomach exit.
- Fatigue and dizziness. Fatigue and dizziness can occur in anemia. The anemia is caused by blood loss in the stomach. The blood loss itself does not need to be noted.
- Black stools. If you have more blood loss, your stool may stain black. The blood dye is converted into a black dye in the stomach and intestines. Iron tablets may also be the cause of black stools.
The symptoms do not have to indicate stomach cancer. They can also be caused by other conditions. If you have complaints for 3 to 4 weeks, please go to your GP. Even if you have a black stool for several days and do not use iron pills.
Surviving stomach cancer
Of the patients with stomach cancer stage 1, after 1 year more than 80% and after almost 3 years, almost 70% live. In patients with stage 4 stomach cancer, less than 20% after 1 year is still alive. The survival of stomach cancer has hardly been improved over time.
Stomach cancer risk factors
The exact cause of stomach cancer is unknown. There are, however, factors that increase the risk of stomach cancer.
Infection with bacteria
A greater risk of stomach cancer is caused by infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. This bacterium can cause chronic inflammation of the stomach wall and stomach ulcers. Many years later this can lead to stomach cancer.
The Helicobacter pylori are transmitted by mouth and contaminated food. Infection with this bacterium does not mean that you automatically get stomach cancer.
Contamination with Helicobacter pylori is less common in the Western world. As a result, the number of people with stomach cancer decreases in developed countries.
Lifestyle
The number of lifestyle factors increase or decrease the risk of stomach cancer:
- Smoking increases the risk of stomach cancer.
- Excessive alcohol consumption increases the risk of stomach cancer.
- The Mediterranean diet has a protective effect against stomach cancer. This eating pattern contains a lot of vegetables, fruits, cereals, fish, oil and whole grain products. And little (red) meat and milk products.
- High consumption of smoked and salted foods seems to increase the risk of stomach cancer. This only applies if you are infected with the Helicobacter pylori bacteria. It is mainly about eating processed meat, such as hamburgers, sausages, ham, and bacon. These products can damage the stomach wall. This can cause an infection with this bacterium to occur faster. The stomach may also become more susceptible to carcinogens.
A number of medical conditions may increase the risk of stomach cancer.
Removal of part of the stomach
As a result, there is a higher risk of cancer in the remaining part of the stomach. This is because less gastric acid is made. As a result, more bacteria can grow in the stomach. These can help to produce more chemicals that can increase the risk of stomach cancer.
Insufficient gastric acid
Gastric acid is a juice in the stomach that consumes the food. Too low levels of gastric acid is a risk factor for gastrointestinal cancer. It can also cause other complaints, such as pernicious anemia. This is a condition in which patients do not adequately take vitamin B12 from the diet. As a result, they have an increased risk of anemia: a lack of red blood cells.
The insufficient gastric acid may have different causes. The medical term for insufficient stomach acid is achlorhydric.
Gastroesophageal reflux
In this condition, gastric acid rises in the esophagus. This increases the risk of cancer at the transition between gastrointestinal and esophagus.
Chronic atrophic gastritis
This is a chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract.
Adenomatous polyps in the stomach
Adenomatous polyps are benign swings. In the stomach, they rarely occur. Most people with polyps in the stomach have the hereditary disorder polyposis.
Hereditary cancer for stomach cancer
About 5% of people with stomach cancer get the disease through a hereditary plant. There are families with hereditary cancer for stomach cancer.
Also, there are some rare hereditary conditions that can cause various tumors, including stomach cancer. It is usually about Lynch's syndrome.
If you have questions about heredity in the event of your illness, please discuss it with your GP or specialist.
Not contagious
Cancer is not contagious. Also stomach cancer not. Also by saliva, vomiting or stools, you can not get infected.
Treatment of stomach cancer
The stage of your cancer helps your doctor to decide what treatment you need. Treatment also depends on:
- your type of cancer (the type of cells cancer started in)
- where the cancer is in your stomach
- other health conditions
- Surgery: if the tumor and possible sores in the lymph nodes can be completely removed and your condition is sufficient
- Chemotherapy: usually before and after surgery if your condition is sufficient or to reduce complaints
- Irradiation: in combination with chemotherapy (chemoradiation) after surgery, or to reduce complaints
- Targeted therapy: as palliative treatment, in combination with chemotherapy
*Image source : Gleneagles Hospital
References :
Post a Comment for "Stage 4 Stomach Cancer Symptoms"