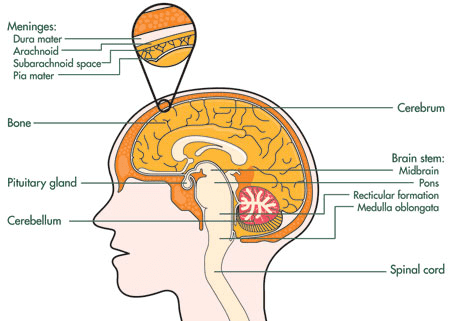
Brain Cancer In Child
The medulloblastoma, the most common malignant form of brain cancer in child, is not one type of swallow but a collective name for five different types of tumors. Each variant has its own characteristic gene expression pattern, abnormalities, and clinical properties. Scientists led by the AMC's Anthropogenetics department identified the molecular genetic features of each type of medulloblastoma. The new classification, according to the staff member and researcher Marcel Kool and professor of Anthropogenetics Rogier Versteeg, should eventually lead to a better, because of more patient-tailored treatment.
Scientists from the Netherlands, Germany, Great Britain, and Poland investigated the biological characteristics of malignant brain cancer in child, called medulloblastomas. Based on gene expression profiles, they conclude that there are five different types of medulloblastomas, each having their own characteristics. Type A, for example, affects some older children and is characterized by mutations in the beta-catenin gene. This variant is relatively small. For the other four types (B, C, D, and E) there are mutations in other genes. Also, more frequent metastases occur, especially in C, D and E tumors. Type A has the best forecast.
The new molecular-biological classification allows a better estimate of the risks to the patient. Therapy can then be adjusted accordingly. For patients with medulloblastoma type A, this could mean, for example, that less toxic treatment with fewer side effects suffers.
About 20% of brain cancer (tumors) in child are medulloblastoma. Incidence of medulloblastoma lessens with age. Approximately 70% of all cases occur in child under age 10. Approximately 250 to 500 children in the United States receive diagnosis medulloblastoma annually. The treatment consists of a combination of surgery, radiotherapy (radiation) and chemotherapy. About half of the children with this type of cancer die. Patients who are well-cured, and especially children of very young age, often suffer from adverse effects of therapy. Growth and concentration disorders are common, but also infertility, hormone malfunction and other forms of cancer.
Scientists from the Netherlands, Germany, Great Britain, and Poland investigated the biological characteristics of malignant brain cancer in child, called medulloblastomas. Based on gene expression profiles, they conclude that there are five different types of medulloblastomas, each having their own characteristics. Type A, for example, affects some older children and is characterized by mutations in the beta-catenin gene. This variant is relatively small. For the other four types (B, C, D, and E) there are mutations in other genes. Also, more frequent metastases occur, especially in C, D and E tumors. Type A has the best forecast.
The new molecular-biological classification allows a better estimate of the risks to the patient. Therapy can then be adjusted accordingly. For patients with medulloblastoma type A, this could mean, for example, that less toxic treatment with fewer side effects suffers.
About 20% of brain cancer (tumors) in child are medulloblastoma. Incidence of medulloblastoma lessens with age. Approximately 70% of all cases occur in child under age 10. Approximately 250 to 500 children in the United States receive diagnosis medulloblastoma annually. The treatment consists of a combination of surgery, radiotherapy (radiation) and chemotherapy. About half of the children with this type of cancer die. Patients who are well-cured, and especially children of very young age, often suffer from adverse effects of therapy. Growth and concentration disorders are common, but also infertility, hormone malfunction and other forms of cancer.
*Image source : Macmillan Cancer Support
References :
Post a Comment for "Brain Cancer In Child"